What Is an Air Handling Unit (AHU)?
An Air Handling Unit (AHU) is the largest and most customized form of commercial air conditioning, typically installed on rooftops or exterior walls of buildings. It houses multiple components within a box-shaped structure designed for air purification, air conditioning, and ventilation. AHUs regulate the thermal condition of the air—controlling temperature and humidity—while ensuring filtration and cleanliness. Through an extensive duct network, conditioned air is distributed throughout various rooms. Unlike standard air conditioners, AHU HVAC systems are specifically designed for each building, integrating internal filters, humidifiers, and other devices to optimize indoor air quality and comfort.
The Role of AHUs in Commercial Industrial HVAC Systems
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (Commercial Industrial HVAC) systems are crucial for maintaining optimal ventilation and air quality in large buildings. AHUs are generally mounted on rooftops or outside walls, distributing conditioned air via ducts to different rooms. Each AHU system is tailored to the building’s specific requirements for cooling, heating, and ventilation.
Applications of HVAC Air Handling Units
HVAC air handling units are vital for maintaining air cleanliness and controlling CO2 levels in high-traffic areas such as shopping malls, theaters, and conference halls. By bringing in fresh air, they help reduce the number of blower fans needed, saving on energy costs while ensuring compliance with air quality standards. Critical environments like cleanrooms and operating rooms require precise temperature control and hygiene, often achieved with dedicated fresh air handling units. Facilities handling combustible gases benefit from explosion-proof AHUs that safeguard against gas explosions.
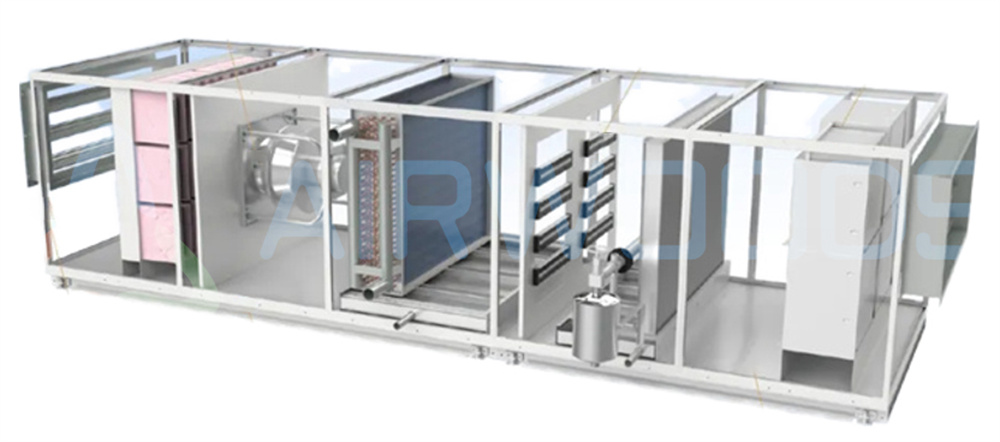
Key Components of an Air Handling Unit
Air Intake
Custom air handling units draw in outside air, filtering, conditioning, and circulating it inside the building. They can also recirculate indoor air when appropriate.
Air Filters
Air filters capture airborne pollutants such as dust, pollen, and bacteria. Specialized filters are used in areas like kitchens and workshops to manage specific contaminants and prevent buildup.
Fan
The fan is the core of the HVAC air handling unit, responsible for distributing air into the ductwork. Fan types—such as forward-curved, backward-curved, and airfoil—are selected based on static pressure and airflow requirements.
Heat Exchanger
The heat exchanger enables thermal transfer between air and coolant, adjusting the air temperature as needed.
Cooling Coil
Cooling coils lower the air temperature by using water droplets, which are collected in a condensate tray to manage humidity.
Energy Recovery System (ERS)
ERS units enhance energy efficiency by transferring thermal energy from exhaust air to incoming fresh air, minimizing additional heating or cooling needs.
Heating Elements
Electric heaters or heat exchangers can be incorporated into the AHU to further regulate indoor temperatures.
Humidifier and Dehumidifier
These components control indoor humidity levels to ensure a comfortable and healthy environment.
Mixing Section
The mixing section blends indoor and outdoor air to maintain optimal air temperature and quality while reducing energy consumption.
Silencers
Silencers minimize noise generated during fan and component operation, maintaining a pleasant indoor environment.
Importance of Energy Efficiency in AHU Systems
Energy efficiency is a critical feature of modern AHUs. Since 2016, the European Ecodesign Regulation 1235/2014 mandates energy-efficient designs. Heat recovery systems in AHUs mix indoor and outdoor air to reduce the temperature difference, significantly lowering the energy needed for air conditioning. Variable speed fans further improve efficiency by adjusting airflow to meet real-time demands, making the system more adaptable and less energy-intensive overall.